What Is a Reefer Container and Where Did the Term Come From?
The word “reefer” comes from “refrigerated container” and became common in the shipping industry in the 1960s. Early reefers relied on external cooling, but by the 1970s, self-powered units with built-in refrigeration and insulation became standard. Today, the term refers to any container designed for consistent temperature control across long distances.
Many businesses ask what is a reefer container when exploring cold chain options. Simply put, it’s a specially designed shipping container reefer unit used in temperature-controlled logistics. .shipping unit used to transport perishable or climate-sensitive goods. These containers offer:
- Integrated refrigeration systems for precise cooling or heating
- Insulated walls to prevent temperature fluctuations
- Ventilation and humidity controls for added cargo protection
- Monitoring systems to track conditions in real time
What Is a Refrigerated Container ?
A refrigerated cargo container , also referred to as a “reefer box,” is a modular unit that transforms a standard shipping container into cold storage using an external cooling source.
- Temporary or seasonal use
- Flexible on-site cold storage
- Multi-purpose transport needs
What Is a Reefer Container vs. a Refrigerated Container: Key Differences Explained
To make the right choice for your cold chain needs, it's important to understand what is a reefer container is and how it performs differently from a traditional refrigerated container in real-world applications.
1. Temperature Control
Reefer containers are equipped with integrated refrigeration units, providing precise and consistent temperature control throughout the shipment. They are ideal for maintaining strict environmental conditions, regardless of external temperatures.
Refrigerated containers, by contrast, depend on external cooling systems. While they still offer reliable temperature control, their adaptability to different cooling technologies makes them better suited for broader, less critical applications.
2. Type of Commodities
Refrigerated containers are typically used for frozen or semi-frozen goods such as meat, seafood, or processed foods that must remain solid during transit.
What is a reefer container used for ? It is ideal for highly perishable items like fresh produce, dairy, flowers, and pharmaceuticals, where precise temperature control is essential. where even minor temperature fluctuations can compromise quality or safety.
3. Design and Construction
Reefer containers are self-contained systems with built-in insulation and cooling units. They’re designed specifically for international shipping and long-haul routes, with technology that monitors and maintains internal conditions in real time.
Refrigerated containers are modular in design. They’re essentially standard shipping containers that can be converted into cold storage using external refrigeration units. This makes them a flexible choice for short-term use or on-site cold storage.
4. Power Source
Reefer containers require continuous external power, supplied by vessels, port facilities, or onboard generators, to operate their internal refrigeration systems.
Refrigerated containers can be powered by various sources, including diesel gensets or solar-powered units, offering enhanced flexibility in remote or off-grid areas.
5. Cost and Use Flexibility
Many businesses ask how much a refrigerated container costs when comparing cold chain options. Refrigerated containers are generally more cost-effective due to their simpler design. and the ability to attach to standard containers. They’re a great solution for businesses needing temporary cold storage or budget-conscious cold chain options.
Reefer containers, while more expensive, deliver reliable performance for critical cargo. Their advanced technology ensures goods arrive fresh and uncompromised, making them ideal for pharmaceutical, agricultural, and high-value shipments.

How Do Refrigerated Shipping Containers Work?
Cooling System Mechanics
The reefer container refrigeration system uses components such as a compressor, evaporator, condenser, and fan units, all integrated into a self-powered loop to regulate internal temperature with high precision.
Reefer containers use electric-powered refrigeration systems similar to household fridges but on a larger scale. Warm air is pulled in, cooled using a compressor and refrigerant, then recirculated to maintain the
Its integrated reefer container refrigeration system is engineered to maintain internal temperatures across long-haul routes, ensuring cold chain consistency regardless of external climate conditions.
Airflow and Temperature Distribution
Cold air flows evenly through floor ducts, reaching all cargo areas. This prevents hot spots and protects sensitive items like fruits, flowers, and medicine from uneven temperatures.
Smart Monitoring and Control
Modern units include digital systems for setting and tracking temperature in real time. Alerts and remote access help ensure a consistent climate even during long hauls or power interruptions.
Temperature Ranges in Reefer Containers
Cooling, Freezing, and Heating Modes
Reefer containers typically operate from -30°C to +30°C. This wide range makes them suitable for chilling fresh produce, freezing meat or seafood, or warming items that must not drop below room temperature.
Recommended Temperatures by Cargo Type
- Fresh fruits/vegetables: +2°C to +8°C
- Frozen goods (meat, seafood): -18°C to -25°C
- Pharmaceuticals: +2°C to +8°C
- Chocolate: +15°C to +18°C
- Flowers/plants: +5°C to +10°C
Each cargo type must be matched to the right temperature to avoid spoilage.
Types of Reefer Container: Sizes, Uses & Technical Specs
Now that we’ve answered what is a reefer container is , let’s explore the various sizes and technical specifications available in the market.
There are several types of reefer container available to meet different cold chain needs, depending on volume, cargo sensitivity, and transport duration.
20ft, 40ft, and High Cube
- 20 ft reefer: ~28–29 m³; best for smaller loads or ports with space limits.
- 40 ft reefer: ~58–60 m³; good for large-volume cold chain shipments.
- 40 ft High Cube: Similar to 40 ft but taller (9’6”), ideal for bulky or tall cargo.
Internal Capacity and Insulation
All reefer containers use insulated walls, corrosion-resistant interiors, and airflow-friendly floor designs (like T-bar) to maintain even temperatures. Capacity varies by size but all are optimized for air circulation
To better understand where reefer containers fit within the broader shipping industry, see our full guide on Types of Containers Used in Shipping.
Non-Operating Reefers (NOR): Definition and Usage
Non-Operating Reefers (NOR) are reefer containers used without activating the cooling system. They carry non-perishable cargo on return trips, helping reduce repositioning costs. NORs still offer insulation and structure benefits, making them ideal for dry cargo like textiles, electronics, and general goods when reefer supply is high.
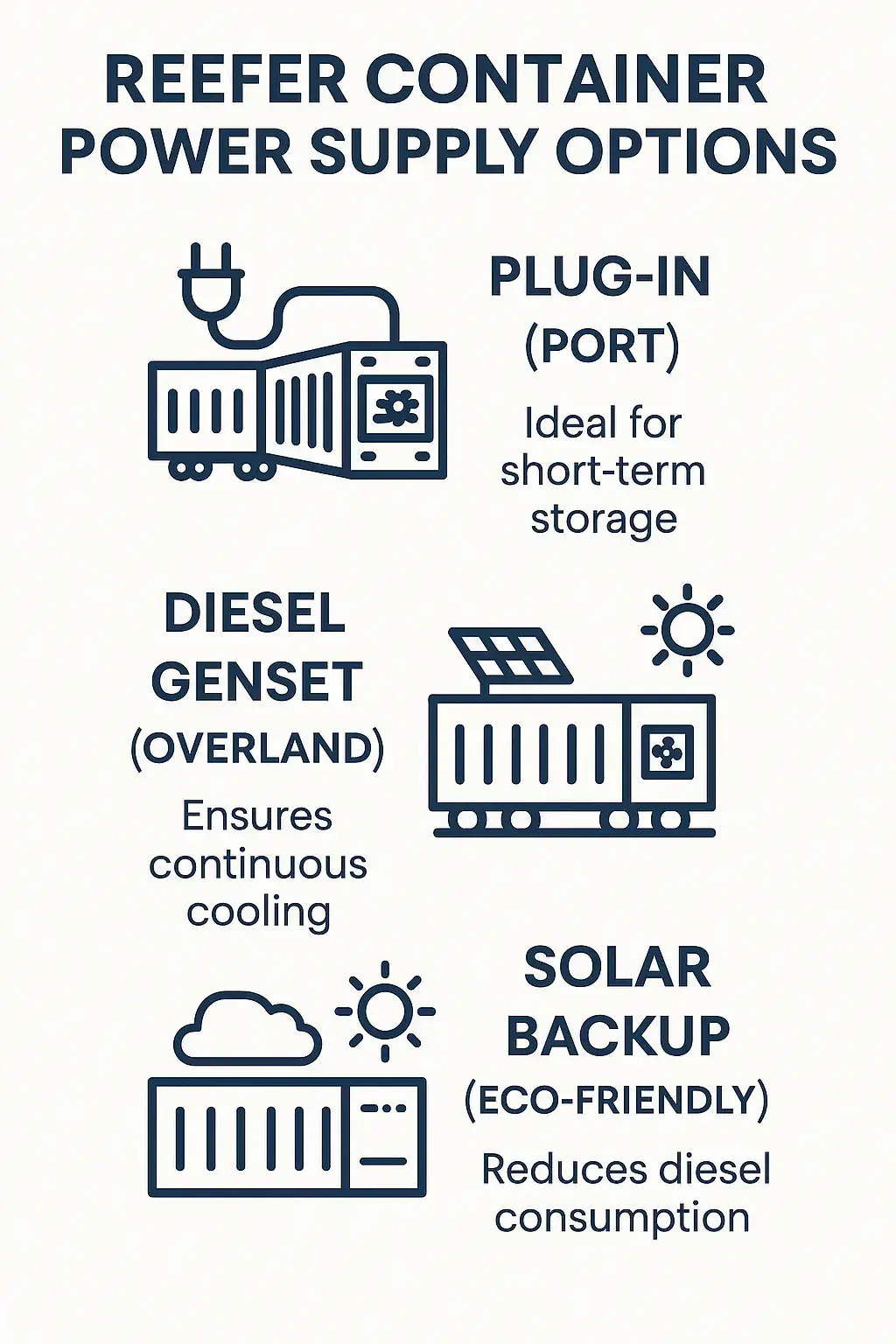
Reefer Container Power Options
Powering refrigerated containers (reefers) depends on the route, cargo sensitivity, and available infrastructure. The main options include:
Reefer Container Power Supply Options : Plug-In, Genset, and Solar
- Plug-in Power: Commonly used at ports or warehouses during short-term storage or port-side operations, where stable electrical connections are available. This is often the preferred method when using a reefer container without genset.
- Gensets (Diesel-Powered Units): Attached to the container for overland or rail transport, ensuring uninterrupted cooling when external power sources are not accessible.
- Solar Power: A sustainable and eco-friendly option, typically used as a backup system to reduce reliance on diesel fuel, especially in reefer containers without gensets.
Choosing the right power source depends on whether you're using a reefer container without genset, the specific temperature control needs of the cargo, and the availability of power infrastructure along the journey.
When to Choose a Reefer vs. a Regular Cooling Container
Product Type – Distance – Customer Budget
Choose reefers for sensitive cargo (like pharmaceuticals, produce, dairy) and long international shipping where exact temperature control is essential.
Choose refrigerated containers for local use. If you're handling frozen items for short distances, a refrigerated cargo container provides an affordable, effective, and flexible solution for budget-conscious operations, short-term, or frozen goods when cost-efficiency is the priority. Budget and cargo type are key in deciding.
Can a Reefer Container Be Modified? When Is It Practical?
Yes, reefer containers can be customized. Modifications include adding lighting, shelving, or alternative power (solar/genset) for use as mobile cold storage. It’s practical when using the container for long-term storage, remote locations, or specialized cargo setups—while maintaining its insulation and cooling integrity.
Best Practices for Using Refrigerated Containers
Cargo Arrangement – Ventilation – Safe Unloading
- Arrange cargo properly to allow airflow; don’t block vents.
- Ventilation ensures even temperature distribution.
- Unload quickly to prevent thermal shock.
- Regular preventive checks help avoid mechanical issues during transit.
Top Manufacturers of Reefer Units
Carrier – Daikin – Thermo King – StarCool
- Carrier: Energy-efficient and widely supported.
- Daikin: Quiet operation and eco-friendly refrigerants.
- Thermo King: Advanced temperature tracking and durability.
- StarCool: Built-in smart technology, ideal for long-distance hauls.
Choose based on budget, cargo needs, and tech features.
Common Challenges in Reefer Shipping and Their Solutions
Reefer logistics face challenges like:
- Temperature fluctuation: Use containers with smart monitoring.
- Customs delays: Work with experienced logistics providers.
- Power outages: Equip containers with gensets or backup plans.
- Wrong container choice: Match container specs to cargo type from the start.
Solving these issues early protects cargo and avoids financial loss.
ACS Logistics Co. your cold chain partner:
At ACS Logistics Co., we understand the complexity of temperature-controlled logistics. Whether you're shipping across the globe or storing goods on-site, we offer:
- Tailored cold chain solutions
- Access to both reefer and refrigerated containers
- Expert support and regulatory compliance
- Advanced tracking and security systems
At ACS Logistics Co., our Sea Freight Services include full support for reefer and refrigerated container shipments, with global coverage, expert handling, and real-time tracking.
We help you make informed choices, so your sensitive cargo arrives in perfect condition every time.
Contact ACS Logistics Co today for smart, secure, and reliable cold chain logistics.
FAQs
Can a Reefer Container Be Converted Into a Refrigerated Container?
No. Reefer containers have an integrated system built into their structure. They are fundamentally different from modular refrigerated units.
Which Option Is More Cost-Effective?
Refrigerated containers are typically more affordable and versatile for general cold storage needs. However, for high-risk, high-value, or sensitive goods, investing in a reefer container ensures better protection and performance.
What Is a Reefer Container vs. Refrigerated Containers